- Find issue to address
- Create and checkout new branch (with the issue ID on its title)
- Apply the fixes (on the new branch)
- Commit the changes (on the new branch)
- Checkout master branch
- Merge changes (from new branch) into master , using the --no--ff (no fast-forward) option (this is very important, see here and here for a good explanation why)
- Push to GitHub
Here is a simple issue to fix: https://github.com/TeamMentor/Master/issues/389
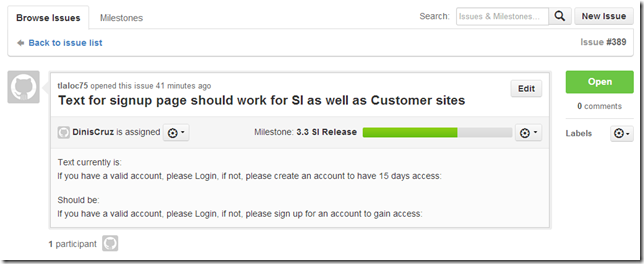
In GitHub, the issue is #389 , so on a local clone of the Master repository, we create a branch called Issue_389 (using the –b switch to create it)

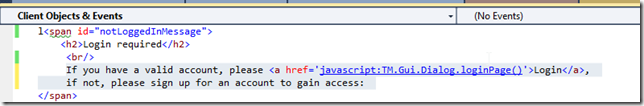
In VisualStudio, apply the fix to the code:
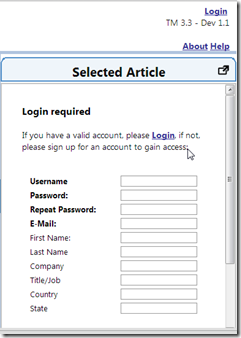
Quickly look in a browser to confirm the change (this should also be reconfirmed via a UI UnitTest):
Commit the change to the Issue_389 branch:

Which means that at this moment, there is nothing else to commit on the Issue_389 branch:

which is now one commit ahead of master

Next step is to checkout (into) master and do the git merge using the --no--ff

Gitk shows the effect of the --no--ff (ie. the use of the branch was preserved)

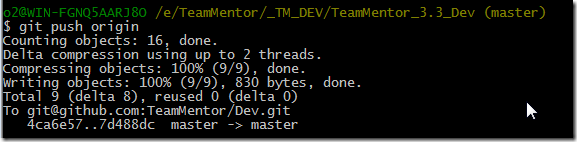
Final step is to push the commits to GitHub:
Here is the commit at GitHub:

Here is the GitHub's Network view:
